Our Diagnostic Services – All Constellations Possible
What is Exome Diagnostics?
Exome diagnostics is the genetic testing approach of choice for patients with complex, heterogeneous, and unspecific symptoms. It supports physicians in stating a diagnosis, often after their patients have experienced years of uncertainty.
The exome comprises all protein-coding regions (exons) of the approximately 23,000 genes in the human genome. Although the exome accounts for only about 1%-2% of the whole genome, about 89% of all known disease-causing variants are located within the exons. Whole exome sequencing allows the simultaneous analysis of genes in any combination. If the exomes of additional family members are also sequenced, as in trio exome diagnostics, an exome-wide segregation analysis can be performed. This approach significantly increases the chances of finding the genetic cause of complex phenotypes in a shorter time compared to genetic testing of small gene sets.
We are committed to identifying the genetic cause of disease for every patient. Therefore, we have developed an innovative diagnostic approach that goes beyond the possibilities of regular exome diagnostics: ExomeFocus® and ExomeXtra® (Single & Trio) offer an efficient solution for every patient scenario and family constellation.
All Achievements of Genetic Testing Integrated Into Our Exome Diagnostics
With the latest update of our ExomeXtra® enrichment, we offer you the most innovative solution in exome diagnostics. Designed to generate the most comprehensive sequencing data, our exome diagnostics provides an unmatched basis for the best genetic diagnostics with outstanding features.
Extra Smart Clinical Design
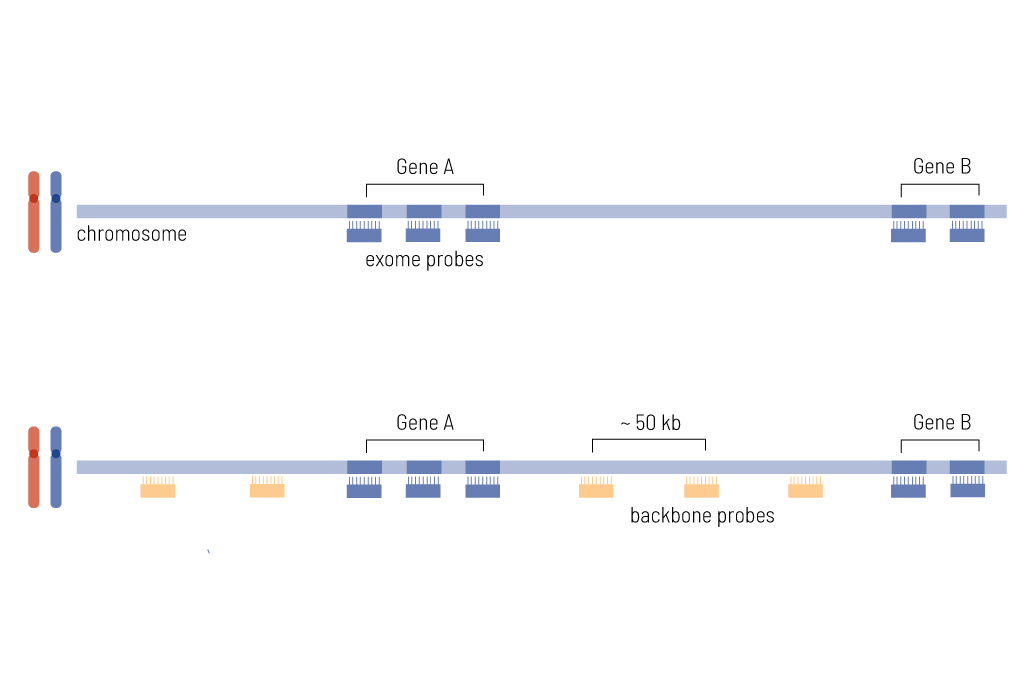
CeGaT’s exome enrichment is the sum of the many years of experience of CeGaT and our collaborators, combined with clinical knowledge. In contrast to standard whole exome sequencing (WES), CeGaT’s proprietary exome design covers not only the coding regions but all known disease-causing regions throughout the genome. With more than 38,000 intronic and intergenic variants, it contains all genomic regions described as disease-related in the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) and ClinVar, the largest public database of genotype-phenotype relationships. In addition, the whole genome is covered with probes at regular intervals to achieve genome-wide array CGH-like CNV calling performance. Our exome enrichment also includes a clinically relevant selection of non-coding RNA genes, flanking intronic sequences, cryptic exons, and the entire mitochondrial genome.
By continuously improving our wet lab process, we have achieved very uniform and complete coverage of all diagnostic targets. To increase sensitivity and to allow us to detect mosaicism, our ExomeXtra® enrichment has an average diagnostic coverage of >100x.
Therefore, CeGaT’s ExomeXtra® provides the ideal basis for genetic diagnostics.
Extra Thorough Analysis
CeGaT’s data analysis goes beyond normal exome diagnostics and increases solution rates. We address copy number variants (CNVs), including compound heterozygous combinations of sequence variants (single nucleotide variants (SNV), small insertions and deletions (indels)) with CNVs. Sequencing data is routinely screened for repeat expansions related to reported phenotypes.
Different family constellations can be analyzed as we can include various numbers of family members in the analysis, such as duo (2) or trio (3). For Trio ExomeXtra® we account for variants in genes with reduced penetrance, variable expressivity and even account for imprinting effects. In trio analysis, we additionally include the detection of uniparental hetero‐ and isodisomies (UPD).
Extra Insightful Results
CeGaT combines human know-how with bioinformatic analysis. The in-house developed software generates data that are evaluated by multiple scientific experts – creating the best possible medical report. CeGaT’s interdisciplinary team of PhDs uses the most recent literature for data interpretation. Complex constellations are discussed with bioinformaticians, and the final report is revised by medical doctors and geneticists to maximize medical usability.
Smarter than Genome
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) is sometimes described as the most comprehensive genetic analysis possible. However, coverage is often too low for reliable variant detection. We sequence our ExomeXtra® with an average diagnostic coverage of >100x, detecting more relevant regions and delivering higher sensitivity than 30x WGS. This increases solution rates and even allows us to detect mosaic variants, which are systematically missed in WGS analyses. At the same time, it avoids thousands of irrelevant variant calls that usually occur in WGS analyses, improving diagnostic speed and accuracy.
Rapid advancement in science is constantly increasing our knowledge about genetic diseases and the potential of genetic analyses. New genomic regions with clinical relevance are identified every year. Our ExomeXtra® enrichment is continuously updated according to the latest clinical findings to always cover all relevant regions. WGS is already a great tool for research. Until it is ready for diagnostic use, ExomeXtra® offers the best combination of WES, WGS and array CGH (comparative genomic hybridization), providing clinical genomic diagnostics to help patients today.
Table 1: Comparision of standard whole genome sequencing (WGS) and ExomeXtra®. Covered refers to average clinically usable coverage after alignment filtering (uniquely mapping, removal of duplicate and overlapping read ends).
WGS | ExomeXtra® | |
Average diagnostic coverage | ~ 30x | ~ 110x |
Total GB sequenced | 100 | 17.5 |
Coding sequences covered > 20x | 93.3% | 98.2% |
Disease-causing non-coding mutations covered > 20x | 96.3% | 98.7% |
Coding sequences covered > 30x | 70.2% | 98.1% |
Disease-causing non-coding mutations covered > 30x | 83.3% | 98.3% |
Detailed Side-by-Side Comparison of Our Diagnostic Services:
Proprietary exome enrichment | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
In-house data analysis and variant calling | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Reported variants of the ACMG classes | 3/4/5 | 3/4/5 | 3/4/5 | 4/5 |
Variant classification with details on ACMG criteria and scale | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Manual gene selection for interpretation | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
IVERP variants* | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓** |
VUS re-evaluation | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
Costs | € | €€ | €€€ | €€€ |
Solving Rate |
* Accounting for variants in genes with known imprinting, variable expressivity and reduced penetrance.
** Prenatal diagnostics with conspicious ultrasound findings.
Additional Services
ACMG Genes
This additional screening of the ACMG genes1 allows the detection of relevant pathogenic variants outside the phenotype in a defined group of genes with therapeutic relevance. In all ExomeXtra®-services, this option is free of charge for the index patient. For ExomeFocus®, it is available at an additional charge. If selected, we issue a separate report for each person indicating our findings within the ACMG genes.
Upgrade ExomeFocus® ExomeXtra® to Trio ExomeXtra®
Trio ExomeXtra® is the test that offers the highest chances of identifying the genetic cause of disease. In cases where the treating physician starts with a singleton exome and later wants to expand to Trio ExomeXtra®, this is offered at a reduced price.
HLA Typing
HLA typing can determine tissue compatibility for allogenous transplants, individual drug response (PGX), and differential diagnosis. HLA typing can also be used to judge susceptibility to disease (e.g., HLA-B27: inflammatory and autoimmune disorders). You will receive an additional report stating the HLA alleles.
Pharmacogenetics
Pharmacogenetic analysis detects genetic changes that influence the efficacy of drugs. If genetic variants affect proteins responsible for the metabolization of substances, their tolerability and efficacy can be severely altered. These drugs include antidepressants, painkillers, neuroleptics, chemotherapeutics, AIDS drugs, thrombosis drugs, anesthetics, beta-blockers, or statins.
A specific enzyme’s reduced activity can lead to increased drug levels at the standard dosage, which is not infrequently accompanied by undesirable side effects. In the case of pharmaceuticals that are only activated by metabolization, the therapeutic effect may be absent altogether. Similarly, increased enzyme activity, due to the resulting increased drug degradation rate, leads to insufficient efficacy of the therapy.
The pharmacogenetics option analyzes known variants in twenty-two genes involved in drug metabolism. If certain gene variants are detected, the treating physician can adjust the therapy individually. With the help of pharmacogenetic analysis, serious side effects can be minimized, and treatment failure avoided.
The “Xtra” in Our Exome Diagnostics
Copy Number Variants (CNVs)
Beside single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions and deletions (indels), copy number variants (CNVs) can also be causative for a particular phenotype. Genetic testing without screening for deletions and duplications is incomplete and may result in incorrect medical reports. All our exome analyses automatically include a deletion/duplication screening – without extra fees. Our CNV analysis in combination with our customized enrichment greatly increases the diagnostic yield.
Our CNV evaluation allows us to detect single exon deletions with a sensitivity of > 81%, larger deletions of three or more exons will be detected with > 96% sensitivity. In addition, we validate our analysis using MLPA or qPCR whenever we find deletions or duplications associated with the patient’s phenotype. The deletion/duplication analysis contributes to CeGaT’s high-quality medical reports to provide you with all available analysis options.
Outside of coding exons, CNV calling covers the whole genome with array‐like resolution of 50 kb (figure 1). This enables accurate characterization and classification of clinically CNVs, allowing the detection of the break points in the intronic region. In order to enable the correct annotation of those structural variants, genome-wide CNV analysis is an essential part of our exome design. Relevant events are included in the medical evaluation. Furthermore, we always determine and describe the quality of the CNV analysis within our medical report. We recommend sending fresh EDTA blood to achieve the highest sensitivity of CNV calling.
Combined Interpretation
CeGaT’s analysis strategy enables us to call CNV/SNV combinations to provide even more detailed and important information. SNV/CNV combinations are defined as occurrences of both a SNV and a CNV in the same gene and at least one of them being ACMG class 4 or 5 (likely pathogenic/ pathogenic).
Screening for Repeat Expansions
To gain the maximum possible insights from our exome dataset, we also screen for repeat expansions in several genes: SCA1 (ATXN1), SCA2 (ATXN2), SCA3 (ATXN3), SCA6 (CACNA1A), SCA7 (ATXN7), SCA17 (TBP), FXN, AR, CSTB, HTT, JPH3, PABPN1. If results indicate a possible repeat expansion that fits the patient’s phenotype, we offer verification with an independent method.
Analysis of Mitochondrial Genome
Mitochondrial genome is included in our enrichment and it is always sequenced. Variants in the mitochondrial genome are evaluated when the phenotype indicates the possibility of a mitochondrial disease. In the case of prenatal diagnostics, the analysis of mtDNA is always included.
VUS Re-Evaluation
CeGaT’s VUS re-evaluation reassesses previously reported variants of uncertain clinical significance (VUS) as soon as new scientific evidence on the pathogenicity of the variant is available. This increases the solution rate of CeGaT analyses.
Genetic research is making great progress and is constantly improving our knowledge of disease-causing variants. Therefore, it is likely that over time a VUS will be better understood and classified as pathogenic (likely pathogenic/ pathogenic) or benign (likely benign/benign).
In the event of such a VUS re-evaluation, CeGaT proactively informs the treating physicians. In addition, the re-evaluated variant is interpreted by our specialists with reference to the patient’s clinical picture and a revised medical report will be prepared, without extra fees (ExomeXtra®). The re-evaluation is critical for the care and treatment of patients and family members.
Sample Case
Patient: boy, 11 months
Clinical symptoms: benign infantile epilepsy with tonic-clonic seizures
Primary report (November 2019): SCN8A c.802A>T (het.) VUS
VUS re-evaluation:
- triggered by HGMD update in Januay 2021
- based on publication Medlin et al., 20202
➔ Variant can now be classified as likely pathogenic. New report has been issued.
References
1 Miller, D. T. et al. ACMG SF v3.1 list for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing: A policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genetics in medicine : official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 24, 1407–1414; 10.1016/j.gim.2022.04.006 (2022).
2iMedlin, L. C., Bello-Espinosa, L. & MacAllister, W. S. Neuropsychological profiles of two patients with differing SCN8A-pathogenic variants. Applied neuropsychology. Child 11, 561–566; 10.1080/21622965.2020.1807983 (2022).
Our Accreditations
Binding standards guarantee the quality of our work: Our laboratory services are accredited according to CAP/CLIA and DIN EN ISO 15189. You can find further accreditations and certifications here.
You Are also Welcome to Take a Look at the Following Areas
Contact Us
Do you have a question, or are you interested in our service?
Diagnostic Support
We will assist you in selecting the diagnostic strategy – for each patient.